價格:免費
更新日期:2018-04-01
檔案大小:83 MB
目前版本:1.2
版本需求:需要 iOS 10.0 或以上版本。與 iPhone、iPad 及 iPod touch 相容。
支援語言:日語
Organic Chemistry Reaction Mechanism is a useful App for learning the fundamentals of reaction mechanism in organic chemistry by using curved arrows. Mastering basic reaction mechanisms is an important survival skill for students learning organic chemistry.
Table of Contents (Total 106 videos)
1. Types of arrows used in organic chemistry
2. Basic principles in organic chemistry
3. Resonance
4. Halogenation of alkanes (Radical reaction)
5. Alkene addition reactions: Electrophilic additions 5-1. Addition of hydrogen halide
5-2. Stability of carbocations
5-3. Supplementary: Rearrangement reaction
5-4. Acid catalyzed addition of water (Hydration)
5-4. Reaction mechanism (How to draw curved arrows)
5-5. Oxymercuration
5-6. Hydroboration
5-7. Addition of halogen (Halogenation): Bromination
5-8. Reaction with peroxyacid (peracid): Epoxidation 5-9. Reaction with osmium tetroxide: Dihydroxidation
5-10. Reaction with ozone: Ozonolysis
5-11. Reaction with hydrogen (Catalytic hydrogenation)
6. Alkyne addition reactions: Electrophilic addition 6-1. Addition of hydrogen halide
6-2. Addition of water
6-3. Addition of halogen (Bromination) 6-4. Addition of hydrogen: Half reduction
6-5. Supplementary: Birch reduction
7. Electrophilic aromatic substitution 7-1. Nitration
7-2. Bromination
7-3. Sulfonation: Sulfonation is reversible !
7-4. Friedel-Crafts reactions 7-4. (A) Friedel-Crafts alkylation
7-4. (B) Friedel-Crafts acylation
7-5. Summary of electrophilic aromatic substitution
7-6. Electrophilic substitution of benzene derivatives 7-6-1. Reactivity
7-6-2. Orientation
7-7. Theory of orientation 7-7-1. Toluene: o,p-directing and activating
7-7-2. Phenol: o,p-directing and activating
7-7-3. Nitrobenzene: m-directing and deactivating
8. Nucleophilic substitution (SN2 and SN1) of alkyl halides 8-1. SN2 reaction
8-2. Reaction mechanism of SN2
8-3. SN1 reaction
8-4. Reaction mechanism of SN1
9. Elimination reaction (E2 and E1) of alkyl halides 9-1. E2 reaction
9-2. Reaction mechanism of E2
9-3. E1 reaction
9-4. Reaction mechanism of E1
10. Reaction of alcohols 10-1. Protonation with strong acids
10-2. Acid-catalyzed elimination of water (Dehydration)
10-3. Reaction with hydrogen halides
10-4. Reaction of allylic alcohols
10-5. Supplementary: Allyllic rearrangement
10-6. Supplementary: Saytzeff’s rule (Zaitsev’s rule)
11. Ethers: Synthesis and Reactions 11-1. Synthesis of ethers-1 11-2. Synthesis of ethers-2: Williamson Ether Synthesis
11-3. Acid cleavage of ethers: Reaction with acids
11-4. Supplementary: Removal of methyl protecting group
11-5. Nucleophilic opening of epoxides with Grignard reagents
12. Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl group (aldehydes and ketones) 12-1. The polarity of the C=O double bond
12-2. Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl group
12-3. Addition of alcohols: Hemiacetal and acetal formation
12-4. Addition of primary amines: Imine formation
12-5. Addition of Grignard reagents
12-6. Supplementary: Addition of Grignard reagents to carbon dioxide
12-7. Addition of acetylides
12-8. Addition of hydrogen cyanide
12-9. Reduction of ketones and aldehydes
13. Esters: Synthesis and Reactions 13-1. Synthetic method for esters-1: Fischer esterification
13-2. Synthetic method for esters-2: Methyl ester formation by diazomethane
13-3. Hydrolysis of esters
13-4. Supplementary: Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of tert-butyl esters
13-5. Reaction with Grignard reagents
13-6. Reduction of esters
13-7. Alcoholysis of esters 13-8. Ammonolysis of esters
14. Enol and Enolate reactions (aldehydes and ketones) 14-1. Keto-enol equilibrium
14-2. Why are a-Hydrogens acidic ?
14-3. Enolization
14-4. Aldol reaction
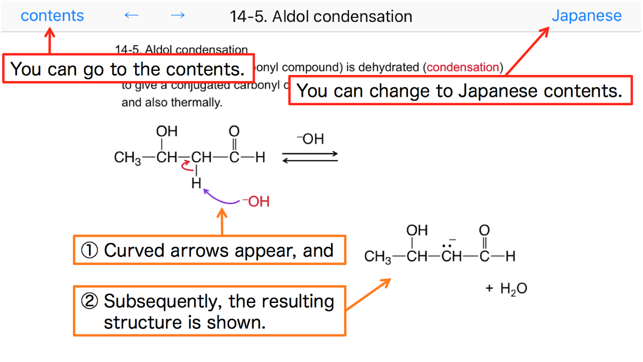
14-5. Aldol condensation
14-6. E1cB reaction
15. Enolate reactions in esters 15-1. Claisen condensation
15-2. Dieckmann condensation and retro-Claisen condensation
15-3. Synthetic methods related to Claisen condensation
15-4. Acetoacetic ester synthesis
15-5. Malonic ester synthesis
16. Michael addition

17. Robinson annulation

支援平台:iPhone, iPad
